Gods and Goddesses
| The ancient world was filled with mystery. Much of what they experienced in the world around them was unknowable and frightening. The ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses represented aspects of the Egyptians’ natural and “supernatural” surroundings and helped them understand its many aspects |
AmonAlso Known as Amen, Amun, AmmonAmun was the chief Theban deity whose power grew as the city of Thebes grew from an unimportant village, in the old Kingdom, to a powerful metropolis in the Middle and New Kingdoms. He rose to become the patron of the Theban pharaohs and was eventually combined with sun god, Ra who had been the dominant deity of the Old Kingdom to become Amun-Ra, King of the Gods and ruler of the Great Ennead. |
|
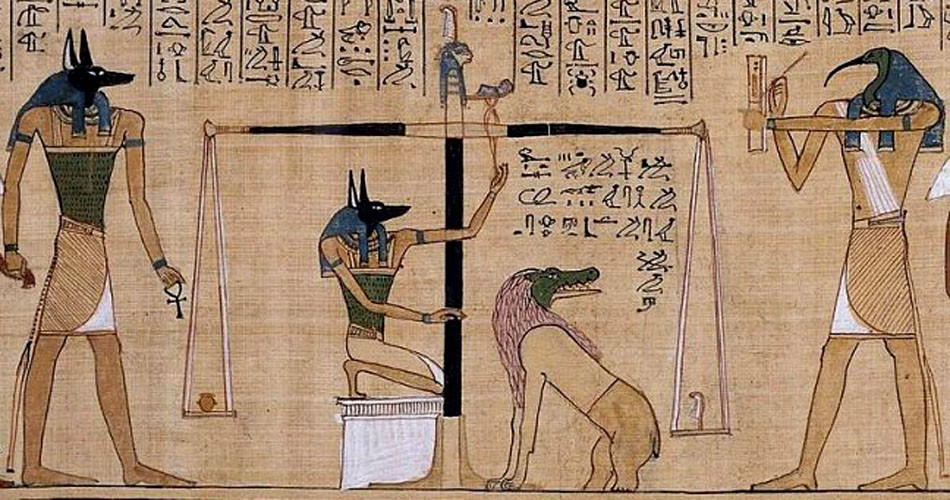
AnubisProtector of the DeadAnubis is shown as a jackal-headed man, or as a jackal. His father was Seth and his mother Nephythys. His cult center was Cynopolis, now known as El Kes. He was closely associated with mummification and as protector of the dead. It was Anubis who conducted the deceased to the hall of judgment |
|
BastetBastet is depicted as a woman with a cat’s head or simply as a cat. Originally an avenging lioness deity, she evolved into a goddess of pleasure.Her cult center was in the town of Bubastis in the Western delta. Many cats lived at her temple and were mummified when they died. An immense cemetery of mummified cats has been discovered in the area |
|
BesUnlike the other gods, Bes is represented full face rather than in profile, as a grotesque, bandy-legged, dwarf with his tongue sticking out. He was associated with good times and entertainment, but was also considered a guardian god of childbirth. Bes chased away demons of the night and guarded people from dangerous animals |
|
HapiHapi was not the god of the river Nile but of its inundation. He is represented as a pot-bellied man with breasts and a headdress made of aquatic plants. He was thought to live in the caves of the first cataract, and his cult center was at Aswan |
|
HathorHathor was the daughter of Ra and the patron goddess of women, love,
beauty, pleasure, and music. She is depicted in three forms; as a cow,
as a woman with the ears of a cow, and as a woman wearing the headdress
of a cow’s horns. In this last manifestation, she holds the solar disc
between her horns. She was the consort of Horus, and her name actually
means “House of Horus.” She had many temples the most famous of which is
at Dendara. |
|
HorusHorus was the son of Osiris and Isis and the enemy of the wicked God
Seth. He is depicted as a hawk or as a man with the head of a hawk.
Sometimes he is shown as a youth with a side lock, seated on his
mother’s lap. He was the god of the sky and the divine protector of
kings. |
|
IsisIsis was the wife of Osiris and mother of Horus. She was associated with funeral rites and said to have made the first mummy from the dismembered parts of Osiris. As the enchantress who resurrected Osiris and gave birth to Horus, she was also the giver of life, a healer and protector of kings.Isis is represented with a throne on her head and sometimes shown breastfeeding the infant Horus. In this manifestation she was known as “Mother of God.” To the Egyptians she represented the ideal wife and mother; loving, devoted, and caring. |
|
MaatMaat was the goddess of truth and justice, embodying the essential harmony of the universe. She was depicted as a seated woman wearing an ostrich feather, or sometimes just as the feather itself. Her power regulated the seasons and the movement of the stars. Ma’at was the patron of justice and the symbol of ancient Egyptian ethics, so the Vizier who was in charge of the Law Courts went by the title Priest of Maat. |
|
OsirisOsiris was originally a vegetation god linked with the growth of crops.
He was the mythological first king of Egypt and one of the most
important of the gods. It was thought that he brought civilization to
the race of mankind. He was murdered by his brother Seth, brought back
to life by his wife Isis, and went on to become the ruler of the
underworld and judge of the dead. |
|